Avoid chainsaw kickback by using the correct handling techniques and utilizing a saw with kickback-reducing features. Always hold the saw firmly with both hands and stand to the side of the cutting path.
Chainsaw kickback occurs when the saw’s bar nose or tip touches an object, or when the wood closes and pinches the chain during a cut, causing the saw to jerk upwards and backwards towards the user. This dangerous reaction can lead to severe injuries.
Ensuring your safety starts with proper chainsaw selection; look for models with built-in safety features like low-kickback chains and inertia-activated chain brakes. Regular maintenance, including chain sharpening and tensioning, also plays a vital role in preventing kickback. Before operating a chainsaw, familiarize yourself with the user manual, and always wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves, eye protection, and a helmet. Understanding and respecting the power of the chainsaw is crucial for safe operation and kickback avoidance.
Recognizing Chainsaw Kickback
Chainsaw kickback can happen in a blink. You need to know what it looks like to stay safe. Kickback is when the tip of the chainsaw blade catches on something and jerks back towards you, which can be dangerous. Understanding how kickback happens is a big step in avoiding it.
Defining Kickback
Kickback occurs swiftly and fiercely, making it a leading cause of chainsaw accidents. Imagine the saw’s nose hitting an object; it recoils back towards the operator.
The result? A potentially uncontrolled and dangerous movement that requires immediate reaction. To use chainsaws safely, you must know what kickback feels like and looks like.
Kickback Triggers
Several factors lead to kickback. Each one can turn a regular cutting job into a risky task:
- Touching the tip: The chainsaw’s nose, or ‘kickback zone,’ is most prone to causing kickback.
- Improper use: Using a chainsaw above shoulder height increases risk.
- Pinching the blade: Cutting at an awkward angle may pinch the chain, leading to sudden jerkback.
- Using a dull chain: A dull or improper chain can catch and cause unanticipated motion.
Each of these triggers sets the stage for kickback. Knowing them helps prevent the snap-back reaction.
| Trigger | Description | Prevention Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Tip Contact | Chain contact at tip | Keep the zone clear |
| High Position | Using saw above shoulder | Cut at waist level |
| Pinch Point | Chain pinched during cut | Use proper cutting angles |
| Dull Chain | Chain not sharp enough | Regularly sharpen the chain |
In summary, chainsaw kickback is not to be underestimated. Recognize what causes it and practice precautionary steps for a safer cutting experience.
The Importance Of Chainsaw Knowledge
Handle chainsaws with wisdom to stay safe. Proper knowledge helps you understand how a chainsaw works. This includes the do’s and don’ts. Mastering this avoids dangerous kickbacks.
Training and practice make you proficient. They equip you with strategies to minimize risks. You learn the correct posture and grasp. These are key to operating safely.
Risk Factors For Operators
- Lack of experience: More experience, less risk.
- Inappropriate stance: Balance and footing are crucial.
- Defective equipment: Regular check-ups prevent malfunctions.
Statistics On Chainsaw Accidents
| Year | Injuries | Fatalities |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 15,000+ | <100 |
| 2021 | 14,000+ | <100 |
This data showcases the real threats felt by chainsaw users. It stresses the need for more awareness and training.
Preventive Measures
Preventive Measures play a pivotal role in ensuring safe chainsaw use. Chainsaw kickback can lead to serious injuries. Taking steps to prevent it is crucial for any chainsaw operator. Recognizing the right equipment and adhering to maintenance protocols can significantly reduce the risk.
Proper Chainsaw Selection
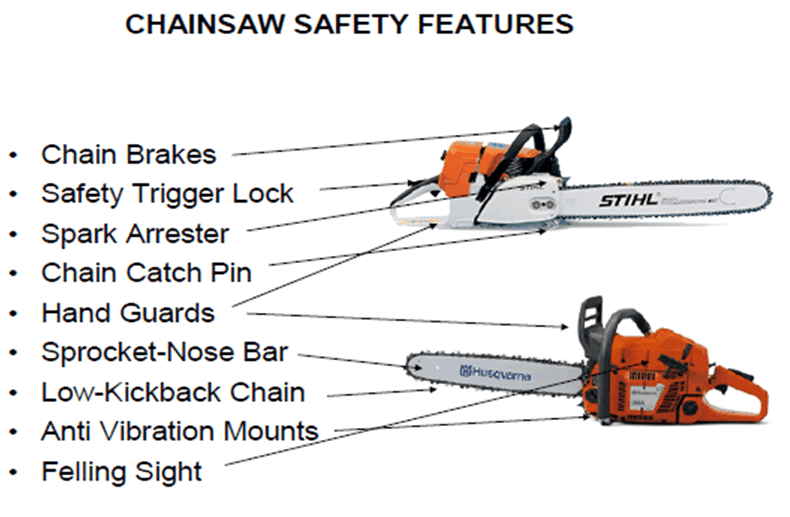
Choosing the right chainsaw is the first step in minimizing kickback. A suitable chainsaw matches the task at hand and the user’s experience. For beginners, opting for a chainsaw with built-in safety features is essential. These features may include a chain brake, anti-vibration handles, and a low-kickback chain.
Using Low-kickback Chains
Low-kickback chains are designed to reduce the risk of sudden upward motion. These chains have specific features like safety links and small cutter profiles. They work by limiting the depth of the cut. This design helps in preventing the chain from getting stuck and causing kickback.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is essential for chainsaw longevity and safety. Ensure the following are checked and acted upon:
- Chain sharpness: A dull chain can increase kickback risk and must be sharpened.
- Chain tension: Too loose or tight can lead to problems. Adjust the tension properly.
- Cleanliness: Remove dirt and debris from the bar and chain.
- Lubrication: Keep the chain lubricated to ensure smooth cuts and reduce kickback potential.
Sticking to a consistent maintenance routine will make a significant difference in preventing chainsaw kickback.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Handling Techniques
Handling a chainsaw with the right technique is key to safety. Chainsaw kickback can happen fast. Knowing how to hold and use your chainsaw is important. Let’s look at ways to stay in control and reduce the risk of kickback.
Grip And Stance
A strong grip and proper stance provide the foundation for safe chainsaw use. Here is how to handle your tool effectively:
- Hold tight: Always grip the chainsaw handles firmly with both hands.
- Bend your knees: Stand with your knees slightly bent to absorb any movement.
- Position your feet: Keep them shoulder-width apart for a balanced stance.
- Stand to the side: Never stand directly behind the saw to avoid the line of kickback.
Cutting Do’s And Don’ts
To minimize the risk of kickback while cutting, follow these guidelines:
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use a sharp chain. | Cut with the tip of the bar. |
| Start cuts with full throttle. | Apply too much pressure. |
| Keep firm footing. | Saw above shoulder height. |
| Follow a cutting plan. | Use a damaged or loose chain. |
Remember to always be mindful of the chain’s path. Keep the chain moving. Never twist the saw during a cut. These tips help prevent sudden movements that can lead to kickback.
Safety Equipment Essentials
Preventing chainsaw kickback starts with wearing the right safety gear. Kickback causes sudden, upward motion. Proper equipment protects you. Always gear up before starting your saw.
Protective Gear
Full-face safety helmets guard your head and face. A visor or goggles protect your eyes from flying debris. Heavy-duty gloves shield your hands. They provide a better grip too.
Chainsaw chaps or pants prevent cuts to your legs. They stop the saw’s blade upon contact. Wear boots with non-slip soles for stable footing. Ear protection muffs keep loud noises from harming your hearing.
Recommended Accessories
Add these accessories to boost safety:
- Anti-vibration gloves reduce hand fatigue. They lessen the risk of losing control.
- Felling wedges help cut trees in the right direction. Safe directional falls are crucial.
- First aid kits are must-haves. They help manage any immediate injuries.
Never underestimate safety importance. These essentials can save lives. Let’s respect the power of chainsaws. Always opt for quality when choosing safety gear. Your well-being deserves it.

Credit: smallfarms.cornell.edu
Operators’ Education And Training
Operators’ Education and Training plays a significant role in preventing chainsaw kickbacks. Proper education ensures operators understand both the risks and the correct handling techniques. Training programs not only offer theoretical knowledge but also provide valuable hands-on experience. By focusing on education and training, chainsaw users can minimize accidents and operate safely.
Certified Training Programs
Investing in certified training programs is crucial for chainsaw safety. These programs cover:
- Chainsaw mechanics and maintenance
- Safety features and how they work
- Correct operating techniques to prevent kickback
- Personal protection equipment (PPE) usage
Certified programs are endorsed by safety organizations. They meet set standards. Look for ones that offer both theory and practical sessions. An authorized certification ensures your training is recognized and up to date.
Practical Skill Development
Practical skill development is the key to mastering chainsaw use. Hands-on training teaches:
- Proper stance and grip
- Smooth operation and control
- Safe cutting techniques to avert kickback
Training should include varied scenarios. These include cutting at different angles and tree felling. A well-rounded skill set is a shield against chainsaw kickback.
| Training Aspect | Reason | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Proper Stance | Ensures balance and control | Less risk of kickback |
| Correct Grip | Provides control over the chainsaw | Accurate cuts, reduced kickback |
| Safety Practices | Prevents potential injuries | Safe chainsaw operation |
On-site Precautions
Taking the right on-site precautions can reduce chainsaw kickback risk. Kickbacks happen fast and are dangerous. By being proactive, you can ensure a safer cutting environment. Let’s dive into specific actions to take before revving up your chainsaw.
Surveying The Work Area
Look around before you start cutting. Clear potential trip hazards. Remove rocks, branches, and debris. Identify escape paths. These steps keep you safe if you need to quickly move away.
- Check for electrical lines.
- Note wind direction and speed.
- Determine tree lean and fall direction.
Emergency Preparedness
An emergency plan is a must. Always carry a first aid kit. Ensure everyone knows its location. Have a communication device like a whistle or a phone. Inform others you will be operating a chainsaw. Here’s a quick checklist to help:
| Item | Check Before Starting |
|---|---|
| First Aid Kit | Accessible and stocked |
| Communication Device | Fully charged and in range |
| Protective Gear | All items worn and properly fitted |
- Ensure a quick exit route is always clear.
- Tell someone where you will be working.
- Bring extra fuel in a safe container.
Innovations Reducing Kickback Incidents
Chainsaw kickback poses a significant risk to users. Advanced technologies and design improvements aim to make chainsaw use safer. Let’s explore some of these key innovations.
Technological Advancements
Technological innovations are vital for enhancing user safety. Chain brake systems are classic yet effective features. They stop the chain almost instantly. Low kickback chains reduce energy during kickback events. These chains have unique shapes that guard against sudden jerks. Anti-vibration systems help maintain control by reducing fatigue.
- Chain Brake Systems: These mechanisms detect rapid movements or shifts in position and halt the chain’s rotation to minimize injury.
- Low Kickback Chains: Designed with safety features such as narrow cutters and depth gauges, they ensure less aggressive cuts and, as a result, less kickback.
- Anti-vibration Systems: Vibration-dampening technologies reduce user fatigue, allowing for better control and a lower risk of kickback.
Design Improvements In Chainsaw
Chainsaw design improvements also play a crucial role in reducing kickback. Lightweight materials make chainsaws easier to handle. Improved handles and guards offer better grip. These design features work together to prevent accidents.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Bar Nose Guards | Plastic or metal devices attached to the tip of the chainsaw bar to block contact with objects that may cause kickback. |
| Ergonomic Handles | Handles designed to fit comfortably in the user’s hands, improving control and reducing the likelihood of a kickback. |
| Protective Guards | Guards placed close to the chainsaw’s kickback zone to protect the user’s hands in case of an incident. |
Always wear protective gear and follow safety instructions to minimize risks further.
Legislation And Safety Standards
Understanding the legislation and safety standards is crucial when handling chainsaws. It ensures not only your safety but also compliance with legal requirements. These safety measures can significantly reduce the risk of chainsaw kickback, an often dangerous and sudden occurrence.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies set safety guidelines for chainsaw use. In the United States, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) leads this effort. Europe looks to the European Union directives, while other countries have local agencies.
- ANSI – American National Standards Institute
- ISO – International Organization for Standardization
- CSA – Canadian Standards Association
Compliance With Safety Standards
Adhering to safety standards is not just a legal requirement. It is a responsibility. Chainsaw manufacturers and users must follow these standards to ensure safe operation. The standards affect the design, manufacture, and usage of chainsaws.
| Standard | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 11336-1 | Chainsaw performance requirements | Ensures peak performance with safety in mind |
| ANSI B175.1 | Safety requirements for gasoline-powered chainsaws | Guards users against product defects and operational hazards |
| EN 381 | Protective clothing standard | Mandates quality protective gear to minimize injury risk |
The ANSI standard, in particular, specifies features that help prevent kickback. These include low-kickback chains and guide bars. Chainsaws with these features bear a distinctive safety mark, indicating compliance.
Learning From Past Incidents
Chainsaw kickback is sudden and dangerous. It can cause serious injuries. Knowing past mistakes helps us avoid them.
Case Studies
In-depth case studies reveal common kickback causes. Experts analyze these events. They teach us safe chainsaw use. Here is a summary of key findings:
- Improper Chain Tension: A loose chain increases kickback risk.
- Incorrect Technique: Cutting with the chain tip can trigger kickback.
- Lack of Maintenance: Dull or damaged chains are more prone to kickback.
Real-life Accounts
Real-life accounts tell us true stories. They show the consequences of ignoring safety. Here are some examples:
-
John’s Close Call: He ignored the safety manual. His chainsaw kicked back. Fortunately, he escaped with a minor injury.
-
Amy’s Experience: She handled kickback well. She followed proper techniques. Her training saved her from harm.
-
Mike’s Tale: He maintained his chainsaw poorly. This led to a nasty accident. Regular checks could have prevented it.
Credit: smallfarms.cornell.edu
Frequently Asked Questions For How To Avoid Chainsaw Kickback
What Causes Chain Saw Kickback?
Chain saw kickback occurs when the saw’s tip contacts an object or when the blade gets pinched. Rapid backward motion can result, posing a danger to the user.
How Likely Is Chainsaw Kickback?
Chainsaw kickback can occur frequently without proper use and safety precautions. Operators must always follow safety guidelines to minimize this risk.
What Makes A Chainsaw Chain Low Kickback?
A low kickback chainsaw chain features depth gauges and guard links, which limit the depth of cut and reduce the risk of sudden kickback. These design elements enhance user safety during operation.
What Types Of Lumber Can Cause Kickback?
Warp-prone lumber, such as wet, twisted, or dense hardwoods, often causes kickback. Using these woods with improper saw techniques heightens the risk.
Conclusion
Ensuring your safety when using a chainsaw is paramount. By following proper techniques and gear recommendations, kickback risks can be significantly reduced. Remember to maintain your equipment, stand correctly, and stay focused every second. Embrace these precautions, and your woodworking tasks will be both successful and secure.
Stay vigilant; stay safe.